Work Energy Theorem
Work Energy Theorem: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Work Energy Theorem
Important Questions on Work Energy Theorem
Statement I: A truck and a car moving with equal kinetic energy are stopped by equal retarding force. Both cover an equal distance before stopping.
Statement II: A car moving towards the East suddenly changes its direction towards the North at the same speed. Its acceleration is zero.
A ball is thrown up with of . Calculate the work done by its weight in one second.
If force is always perpendicular to motion
Calculate the work done in joules in increasing the extension of a spring of stiffness from to is
A man was initially at rest. Then he starts walking on a rough horizontal surface. The kinetic energy increase is due to the work done by
A stone of mass falling from height of hits the ground with a speed of . The work done by the gravitational force is
An object A moving horizontally with the kinetic energy of experiences a constant horizontal opposing force of while moving from a place X to another place Y, where XY is . What is the energy of A at Y?
An object of mass at rest is acted upon by a constant force such that it acquires a speed . Calculate the work done by the force on the object.
A variable force acts on body of mass and it changes the velocity of the body from to . Find the work done (in ) on the body by the variable force.
Work energy theorem is applicable for conservative forces only.
A body of mass travels in a straight line with velocity . What is the work done by the net force during its displacement from to ?
Three identical solid spheres move down through three inclined planes all same dimensions, is without friction, is undergoing pure rolling and is rolling with slipping. Compare the kinetic energies at the bottom.
A small block of mass is released from point on a fixed smooth wedge, as shown in the figure. Bottom of the wedge is marked as and at a point , the block will stop moving because the straight path of the floor is rough.
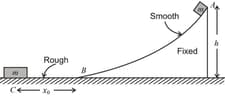
The velocity of the block at the mid-point between to will be
A small block of mass is released from point on a fixed smooth wedge, as shown in the figure. Bottom of the wedge is marked as and at a point , the block will stop moving because the straight path of the floor is rough.
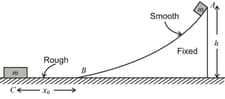
The friction coefficient of the block with the floor is
Identify the tense used in this sentence: 'He had been working for three hours before you arrived.'
Which tense is used in the sentence: 'She will have finished her work by tomorrow'?
Which article of the Indian Constitution guarantees equality of opportunity in matters of public employment?
In which year did the Supreme Court of India deliver the judgement in the Vishaka case that led to guidelines on sexual harassment at the workplace?
Identify the sentence in the present perfect tense.
